The image of American manufacturing is changing. Outdated notions of dingy factories filled with workers toiling away on an assembly line are being replaced by a more accurate portrayal of the modern, high-tech industry. And at the heart of this transformation are five cutting-edge technologies helping manufacturing stay competitive in the 21st century.
3D Printing
3D printing has come a long way since its early days as a prototyping technology. It has now become an essential tool for manufacturers, allowing them to produce prototypes, products, and even entire factories quickly.
The origins of 3D printing can be traced back to the early 1980s when Chuck Hull developed the first 3D printing system known as stereolithography. This allowed users to create three-dimensional objects by building up layers of polymer resin.

In the 1990s, 3D printing began to be used for rapid prototyping, with companies like Boeing using it to test new aircraft designs. In the 2000s, 3D printing began to be used for medical implants and other medical devices. And in the 2010s, 3D printing began to be used for manufacturing products and even entire factories.
Three-dimensional printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is one of the most talked-about technologies in recent years—and for a good reason. This innovative process allows manufacturers to create physical objects from digital files, which can then be used for prototyping or creating finished products. Major companies in various industries are already using 3D printing, and its applications are only growing as technology advances.
Virtual Reality
Virtual reality has come a long way since its early days as a gaming technology. It has now become an essential tool for manufacturers, allowing them to quickly create prototypes, products, and even entire factories.
The origins of virtual reality can be traced back to the early 1960s when Ivan Sutherland developed the first virtual reality system known as the Sword of Damocles. This allowed users to experience a three-dimensional world by wearing a special headset.
In the 1970s, virtual reality began to be used for training simulations. In the 1980s, virtual reality began to be used for medical simulations. And in the 1990s, virtual reality began to be used for gaming and other entertainment applications.
Today, virtual reality is used for various applications in various industries. Major companies in multiple industries are already using VR, and its applications are only growing as technology advances.
While VR is often associated with gaming and entertainment, it also has several potential applications in manufacturing. For example, VR can be used for product design and testing, allowing engineers to understand how a product will look and function in the real world before it’s built. Additionally, VR can be used for training, allowing employees to learn new skills or processes without ever having to step foot on a factory floor.
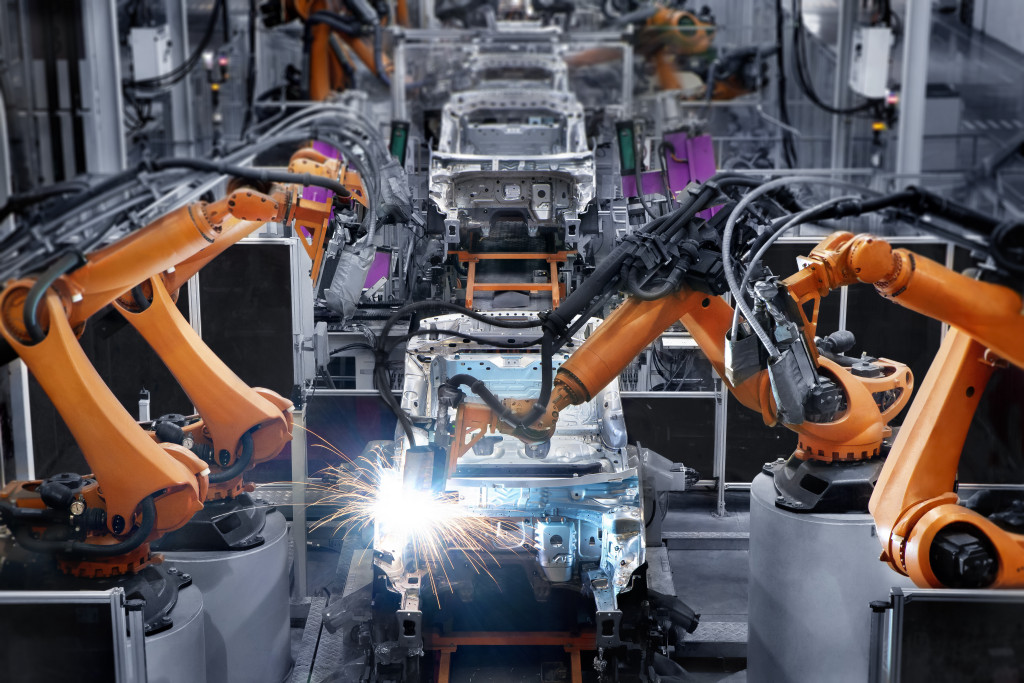
Robotics
Robotics has long been a staple of manufacturing, but they’re becoming increasingly sophisticated thanks to advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. Today’s industrial robots can complete tasks that would have been impossible for their predecessors to perform, opening up new possibilities for automation in manufacturing. Additionally, robotics can help increase safety on the factory floor by reducing the need for human workers to perform dangerous tasks.
Improved Computers
Computers are essential for computing and analyzing data, making them essential for manufacturing. Here are some ways computers are helping in manufacturing.
Improved MRAM
A random-access memory (RAM) that uses magnetoresistive material is known as Magnetoresistive random-access memory (MRAM). MRAM is faster than traditional DRAM and can retain data even when power is lost, making it ideal for industrial applications. A reliable MRAM in industrial computing comes with data security and retention benefits. It’s also much faster when it comes to computing and executing specific programs and protocols. This is because MRAMs in industrial computing are decentralized and autonomous, making them more intelligent than ever.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is a branch of computer science that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations. This type of computing is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to revolutionize manufacturing by allowing for faster and more efficient computing.
Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the growing network of interconnected devices that can communicate with each other and share data over the internet. In manufacturing, IoT technologies such as RFID tags and sensors can track inventory levels, monitor production equipment for signs of trouble, and even automatically reorder supplies when stock runs low—all without human intervention.
These are just a few examples of how manufacturers use technology to enhance operations and stay competitive in today’s economy. As technology continues to evolve, there’s no telling what new applications will be discovered—but one thing is sure: those who embrace change will be well-positioned to succeed in the years ahead.